Road Network Database that comprise various type of data and information.
Road network data includes about 50 types of information, for example, road attribution, traffic regulation, guidance information and more. By combining these various types of data, features such as map displaying, routing and navigation can be added, creating a digital map that is useful in a variety of scenarios.
Continuing from our previous article “What is Road Network Data?” , we introduce what kind of data make up road network data and how it is used, along with some sample database.
Road network data includes about 50 types of information, for example, road attribution, traffic regulation, guidance information and more. By combining these various types of data, features such as map displaying, routing and navigation can be added, creating a digital map that is useful in a variety of scenarios.
Continuing from our previous article “What is Road Network Data?” , we introduce what kind of data make up road network data and how it is used, along with some sample database.

What kind of data are included in road network data?
Road network data can be divided into two main categories: a network of road links (lines) and road nodes (points) with information incorporated in them, and a set of information expressed in order of links that communicate how to get from one point to another.
- Information attached to links (lines) and nodes (points)
Information attached to links is the information of “line” in road network data, or in other words, the information on the roads themselves. For example, various forms of data are maintained including the road class like national roads and prefectural roads, road widths, and the number of road lanes. Also, if a road is a one-way street or closed to traffic, the information is attached to the link (line) as information related to the road. (This information allows the routing features of car navigation systems to determine which roads are one-way streets and which ones are closed to traffic.)
The information attached to nodes (points) is the information assigned to specific spots along the road, such as intersections, which are expressed in the road network data as points. For example, the information includes the names of intersections and the presence of traffic lights.
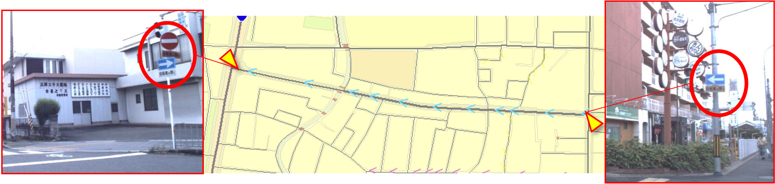
One-way street/Closed to traffic: Expressed as link information that is a part of the applicable interval.
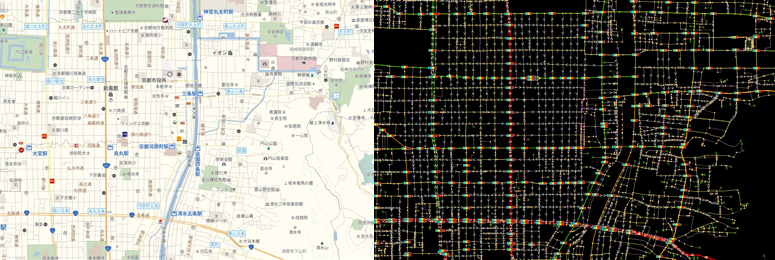
Central Kyoto, Kyoto Prefecture: The city center of Kyoto has many one-way streets.
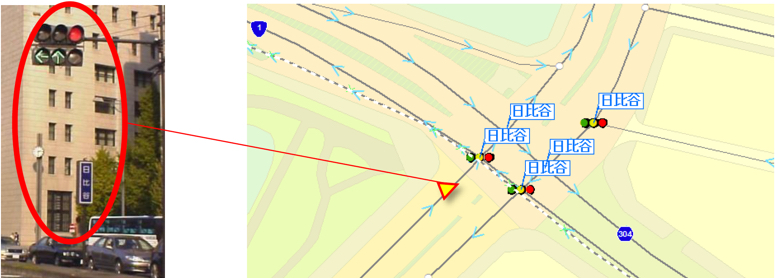
Traffic lights/Names of intersections: Expressed as information of intersections on nodes.
- Information expressed in order of links (lines)
By combining two or more links (lines) connected on the road network data and defining their order (from the departure point to the destination point), directional information can be maintained as data in places like intersections. This includes information on turns prohibition, distance to destination information, and lane information. (Such information allows the navigation features of car navigation systems to determine which direction to go at intersections.)
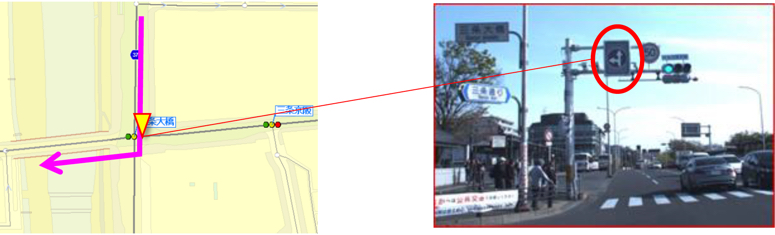
No right turns (traffic allowed only in the designated direction) information at intersections are incorporated in the data.
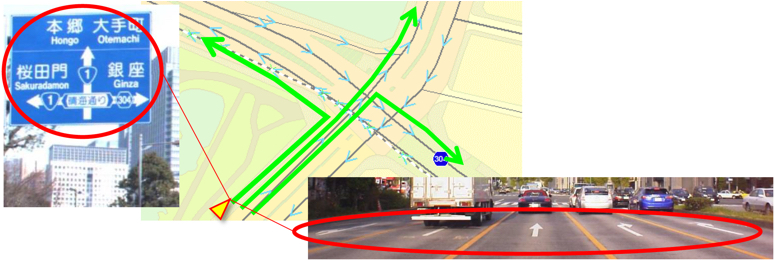
Directional information/Lane information: Data with directions from entering an intersection to exiting it.
At Increment P, we leverage sets of data like these with precision to produce data that accurately represents road information. To enable more accurate routing and navigation, it’s crucial to maintain not only the shapes of roads (links and nodes) but also various information incorporating in them.
Traffic regulation data related to road networks
At Increment P, in addition to general road information such as traffic lights, road regulation signs, and directional signs, we also collect various other road information for specific purposes on a daily basis. We’ll introduce a few examples here.
[Traffic regulation data by vehicle classification]

Vehicle classification regulation signs (right) and types of road regulation signs (left)
[Safety data]
To ensure traffic safety, we at Increment P also maintain data such as 30 km/h zones, flood warning zones, speed limits, and stop signs.
30 km/h zones
The purpose of 30 km/h zones is to ensure the safe passage of pedestrians on commonly used streets by establishing zones and enforcing a speed limit of 30 km/h. Other safety measures are often enforced to control speed within the zones and to discourage drivers from using these zones to cut through traffic. * Refer to the overview on “30 km/h zones” provided by National Police Agency Traffic Bureau
https://www.npa.go.jp/bureau/traffic/seibi2/kisei/zone30/pdf/zone30.pdf
Increment P maintains all information on 30 km/h zones that the National Police Agency provides.

30 km/h zones: 30 km/h zones are displayed based on the National Police Agency’s database.
Flood warning zone data
During heavy rains, some roads become inaccessible due to flooding. Being stranded during such a disaster would be quite a predicament. This is where we use the data on flood warning zones. It can be linked with weather information to warn drivers of areas hit by torrential rain and to avoid certain routes. These data are very valuable during disasters.

Flood warning zones: Detour guidance during torrential rain is also available.
Stop sign data
Increment P’s stop sign data covers all around Japan obtained by driving surveys, using image recognition technology. Stop sign data is used to display stop icons on the map and to alert people visually and sometimes through voice guidance.
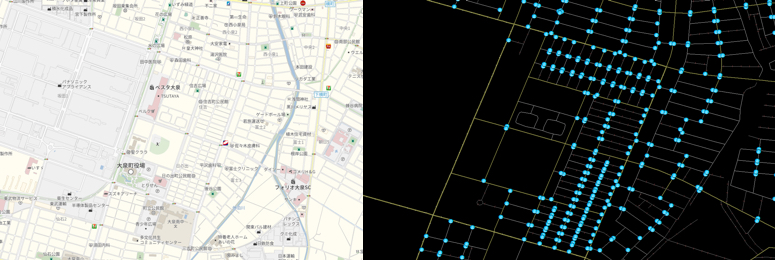
Oizumi-machi, Ora-gun, Gunma Prefecture: Oizumi-machi, Ora-gun has many stop signs.
Speed limit data
Increment P’s speed limit data is associated to each road link and is used to warn drivers who are driving too fast, as well as for routing options in car navigation systems.

Speed limits: Corresponding link IDs and speed limit codes (20 km/h to 120 km/h) are stored.
In addition, our safety data covers other related warning signs such as those for falling rocks and slippery roads. By displaying icons on the map, this data enables alerts to be generated to warn users.
[Road elevation data] [Distance mark data]
We also maintain data related to road elevation and distance marks.
Road elevation data
The elevation of each point along road links (lines) throughout Japan is displayed, including narrow streets.
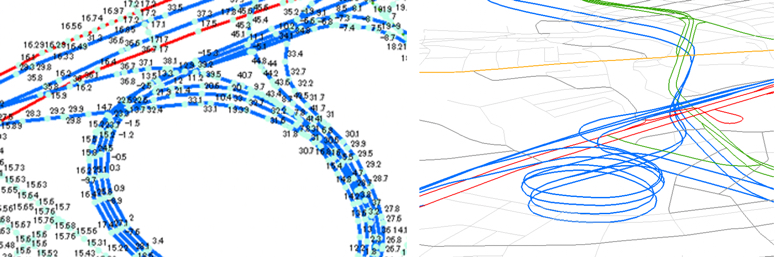
Road elevation: Elevation points are positioned on nodes, composition points, and supplementary points. Available for tunnels and bridges (right).
Distance mark data
Distance mark point data obtained during driving surveys
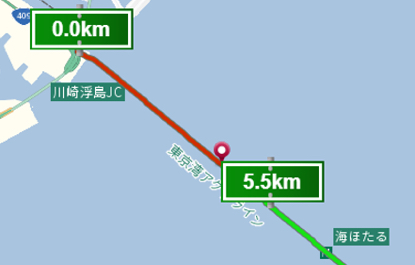
Distance post: Distance posts on expressways for every 100 meters are stored as data.
Try out the truck routing feature on the MapFan Lab Site!
Increment P’s Lab Site lets you see how map data and some of the features that use the data work. Give it a try!
If you want to find routes for a truck that take vehicle sizes into consideration or see traffic regulations by vehicle classification, try the large-size vehicle probe feature and routing by vehicle classification feature.

MapFan Lab Site: the large-size vehicle probe feature and routing by vehicle classification feature powered by FTRD
If you want to check for roads where entry is blocked or roads with blocked turns, try the road regulation data.

MapFan Lab Site: road regulation data
If you want to check the distance to an expressway, try the distance mark feature.

MapFan Lab Site: Distance posts
In this article, we featured Increment P’s road network data and other related data. You may find our road network data, which is maintained by incorporating driving survey images covering roads all around Japan, very useful for your company. If you have any questions about what this road network data can do for you, please reach out to us.
Related articles
What is “Road Network Data?” The present and future of road network data, a crucial component of routing functions
What is “Road Driving Images?” – Increment P’s driving images where all roads in Japan are recorded.
Click here to contact us for inquiry of map database and services.